Artificial intelligence (AI) Concepts
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the intelligence of machines or software, as opposed to the intelligence of living beings, primarily of humans. It is a field of study in computer science that develops and studies intelligent machines. Such machines may be called AIs.
AI technology is widely used throughout industry, government, and science. Some high-profile applications are: advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon, and Netflix), interacting via human speech (such as Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Waymo), generative and creative tools (ChatGPT and AI art), and superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (such as chess and Go).[1]
What is Machine Learning
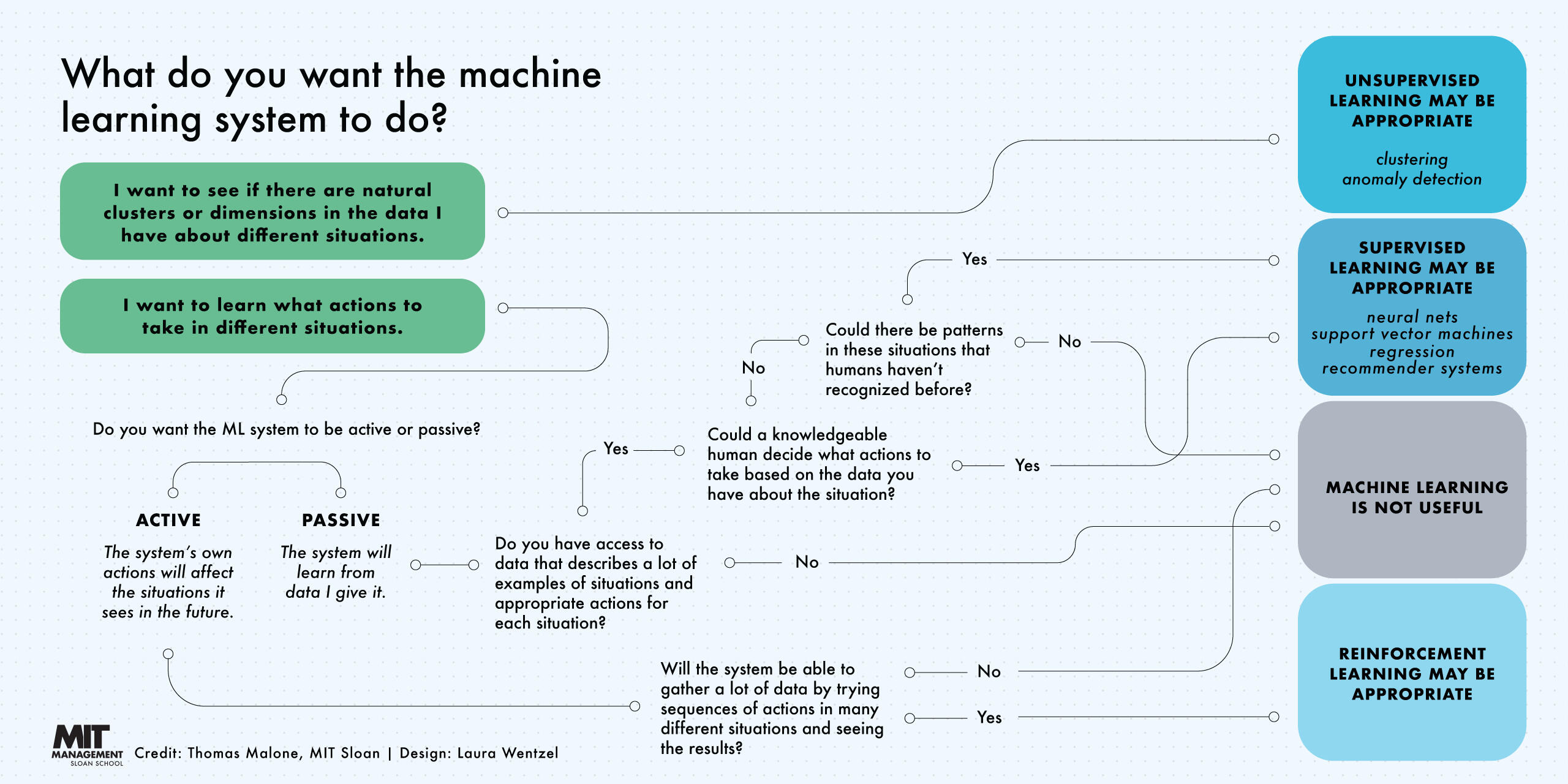
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence, which is broadly defined as the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior. Artificial intelligence systems are used to perform complex tasks in a way that is similar to how humans solve problems.
The goal of AI is to create computer models that exhibit “intelligent behaviors” like humans, according to Boris Katz, a principal research scientist and head of the InfoLab Group at CSAIL. This means machines that can recognize a visual scene, understand a text written in natural language, or perform an action in the physical world.
Machine learning is one way to use AI. It was defined in the 1950s by AI pioneer Arthur Samuel as “the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without explicitly being programmed.”
The definition holds true, according to Mikey Shulman, a lecturer at MIT Sloan and head of machine learning at Kensho, which specializes in artificial intelligence for the finance and U.S. intelligence communities. He compared the traditional way of programming computers, or “software 1.0,” to baking, where a recipe calls for precise amounts of ingredients and tells the baker to mix for an exact amount of time. Traditional programming similarly requires creating detailed instructions for the computer to follow.
But in some cases, writing a program for the machine to follow is time-consuming or impossible, such as training a computer to recognize pictures of different people. While humans can do this task easily, it’s difficult to tell a computer how to do it. Machine learning takes the approach of letting computers learn to program themselves through experience. [2]
What are Multi-agent systems
Multi-agent systems (MAS) are a core area of research of contemporary artificial intelligence. A multi-agent system consists of multiple decision-making agents which interact in a shared environment to achieve common or conflicting goals. MAS research spans a range of technical problems, such as how to design MAS to incentivise certain behaviours in agents, how to design algorithms enabling one or more agents to achieve specified goals in a MAS, how information is communicated and propagated among agents, and how norms, conventions and roles may emerge in MAS. A vast array of applications can be addressed using MAS methodologies, including autonomous driving, multi-robot factories, automated trading, commercial games, automated tutoring, etc. [3]
What are Expert Systems
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if–then rules rather than through conventional procedural code.
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
- https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/machine-learning-explained
- https://www.turing.ac.uk/research/interest-groups/multi-agent-systems
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expert_system
Other pages may be of interest:
📄️ Expert Systems
Introduction
📄️ Machine Learning
Introduction
📄️ Autonomous Agents
Introduction
📄️ Blockchain and AI
Introduction